Industrial scale of wind turbine blade recycling:
China’s wind turbine fleet began to be installed on a large scale after 2004. Given the 20-25 year lifespan of wind turbines , the industry will see its first wave of large-scale decommissioning in 2025, exceeding 1.2 GW and weighing over 10,000 tons of disassembly blades. By 2030, the nation’s wind turbine fleet is projected to exceed 10 GW, with over 10,000 turbines decommissioned and requiring approximately 200,000 tons of blades to be disposed of .
Data shows that by 2030, demand for blade processing will be approximately 30,000 tons, with a cumulative total of approximately 70,000 tons. ( Assuming that each blade weighs approximately 5-6 tons, the group is expected to process approximately 5,000 blades by 2030, with a cumulative total of approximately 12,000. This corresponds to approximately 2,000 wind turbine towers, with a cumulative total of approximately 4,000. )
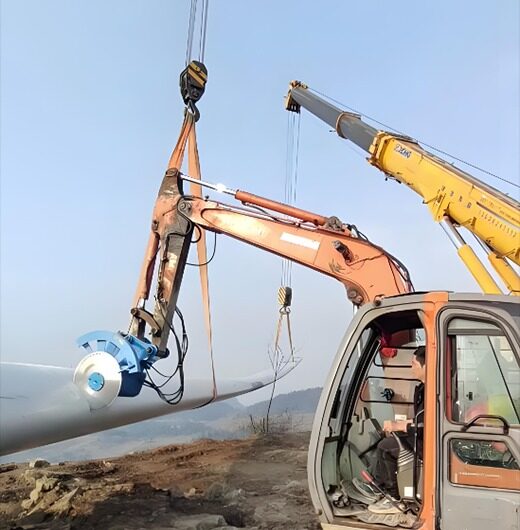


Disadvantages of traditional cutting methods:
Currently, wind turbine blades are generally cut using traditional mechanical methods, such as angle grinders, circular saws, or wire saws . Although some companies are researching large-scale mechanized cutting equipment that uses large saw blades or circular saws for cutting, due to the characteristics of the material and process, most cutting is still done manually with handheld equipment.
Low efficiency:
Data indicates that a team of two to three people takes approximately 3 to 5 days to cut a single blade. The overall cost of cutting a single blade is between 2807.32-4210.98 USD . Furthermore, due to the inherent nature of manual labor and environmental factors , cutting efficiency is reduced.
Environmental pollution and dust problems:
From the perspectives of environmental protection and employee health, mechanical cutting should not be the primary method for large-scale wind turbine blade disassembly in the future. The cutting process generates a large amount of dust, which has a significant impact on the environment and human health. This dust, primarily composed of fiberglass, has a strong adhesive force that adheres to the skin and penetrates into pores, causing intense pain. Inhalation of this dust can have significant consequences for the lungs. Even when wearing protective clothing and dust masks during on-site cutting, inhalation of this dust is unavoidable.
After the initial rough cutting, in order to facilitate transportation by truck, there is a general cutting size standard in the current industry: the finished product size is generally controlled at about 6 meters in length (not exceeding 6 meters) and 1-3 meters in width.

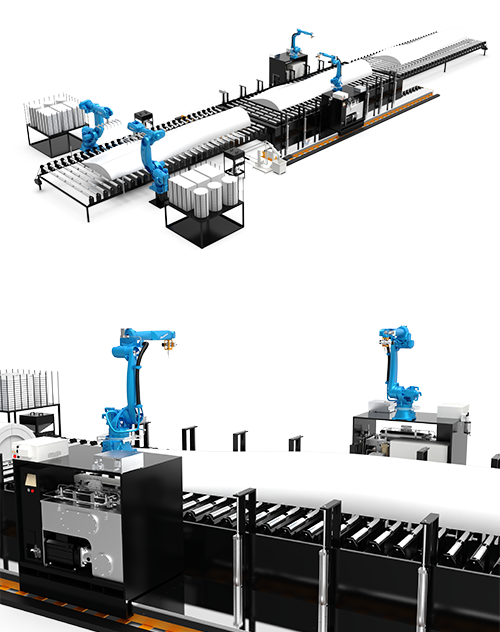
Core cutting high pressure pump: Equipped with two standard 1+N series products, using a 6L/min large flow intensifier to improve overall cutting efficiency.
Cutting actuator – 6-axis industrial robot: The simultaneous use of machine vision with industrial robots and offline programming functions can more widely adapt to scenarios with irregular shapes and where cutting programs cannot be set in advance.
Cutting platform: The effective cutting range is expected to reach 10*5 meters, allowing blades of various sizes to be placed on the platform for cutting, with a certain degree of scalability. Long-distance guide rails are used at both ends of the 10-meter-long side. A motor-driven linear motion mechanism enables the mechanism base to move linearly along the 10-meter direction. Each base is equipped with a 6-axis industrial robot. While the robot arm has a limited reach, the dual-sided guide rails and linear motion mechanism effectively expand its travel range, enabling efficient cutting operations throughout the entire range.
The main goal of the cutting operation is to cut large-scale blade units into strips or blocks as needed. Incorporating machine vision, the incoming material is automatically scanned and analyzed, and the cutting path is automatically generated based on the cutting requirements.
Loading and unloading part: Planned loading is completed by the factory crane; unloading is performed by a robotic arm in conjunction with machine vision, achieving automated loading and unloading ( optional ).
At the same time, the entire system is equipped with a unified central control console, which uses PLC and HMI to build a human-machine interface, and uses industrial standard bus protocols to link high-pressure pumps, robots, auxiliary linear axes, abrasive supply and removal equipment, and uniformly display control operation status, alarm and error information, etc.。
Other supporting equipment needs to achieve Automatic Continuous Abrasive Metering & Feeding System,Abrasive and Water Separation System after cutting, and comply with solid waste discharge standards.
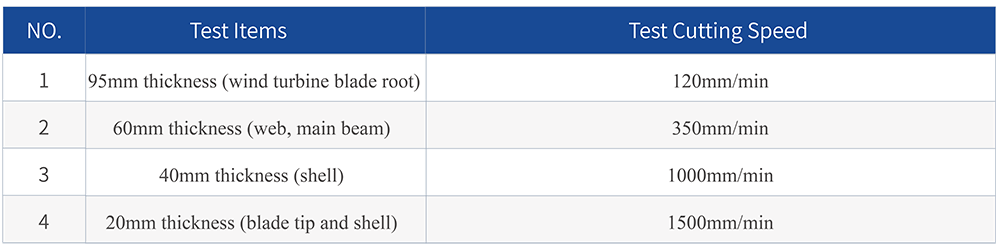
Cutting time and efficiency analysis:
The calculation is based on the following: Using a 1+N series high pressure, 6L/min high pressure pump, 0.4mm orifice, 380Mpa high pressure water pressure, and 80 mesh abrasive, test cutting was conducted on fiberglass wind turbine blade samples of various thicknesses:
Test data table:
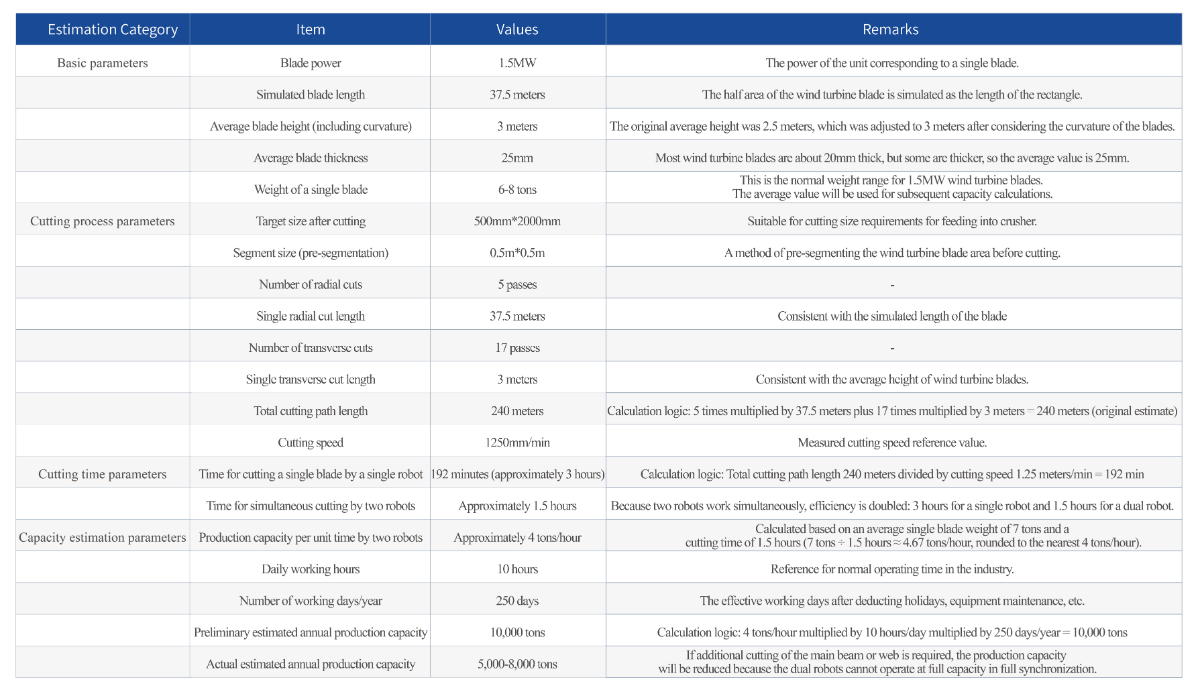
Capacity estimation:
Forplus CNC water jet cutting machines – use water jet technology to enable the green transformation of the wind power industry, Intelligent wind turbine blade factory precision cutting solution, and help build a new circular economy ecosystem.
To be the global top brand waterjet company, with the craftmanship of scientific, rigorous and lean.
Copyright © 2025 Forplus Intelligent Equipment (Chongqing) Co., Ltd.